28 Nonresponse vs Voluntary Response Survey Questions Explained
Explore 25 sample nonresponse vs voluntary response survey questions to improve survey design and understand key differences for better data.
“Nonresponse vs Voluntary Response” might look like boring survey jargon, but it’s actually the secret sauce behind accurate feedback.
Voluntary response is when people choose if they want to reply.
Nonresponse is when randomly chosen folks ignore you.
Why does this matter?
Because it means your data, your budget, and even your reputation can take a hit if the wrong people answer, or don’t.
Whether it’s an online poll, a customer satisfaction email, or that post-purchase “how did we do?” pop-up, knowing the difference changes everything.
On top of that, you’ll see how to use each one, ask smarter questions, avoid bias, and swipe sample questions for your next survey adventure so you do not have to stare at a blank form pretending it is “part of the process.” Try using an online survey maker to streamline the process and ensure higher quality results.
Voluntary Response Surveys (Open Calls & Opt-In Polls)
Voluntary response bias is the elephant in your survey room, easy to invite and surprisingly hard to ignore. These are the surveys where people come to you, not the other way around.
You’re hearing from the people who really care.
Why & When to Use
If you want fast, sizzling feedback, open calls and opt-in polls are your friend. You will hear loudest from your most passionate fans or fiercest critics.
Use these when seeking ideas, tracking social sentiment, or demo-testing new features.
They are quick to launch and do not cost much.
Expect energy and honesty, but less representativeness.
Here’s the thing, this method invites strong opinions but misses the silent bystanders.
Voluntary response bias definition: Your results tilt toward outliers, not your full population.
Mark your reports with a flag so decision-makers do not mistake noisy for normal.
Want a voluntary response bias example? Think about online magazine comment polls where the extremes speak up.
When in doubt, be clear about where your data comes from so nobody over-interprets it.
Clarity about your data source saves you from messy decisions later.
5 Sample Questions
What feature convinced you to sign up for our free beta today?
On a scale of 1 to 10, how strongly do you recommend we add Dark Mode next?
Tell us one reason you follow our brand’s Instagram account.
Which of these taglines grabs you first? (Select all that apply.)
What stopped you from completing your purchase just now?
Plus, voluntary surveys make your super-users feel like VIPs, but you should not expect them to represent your quiet customers.
Super-users love to talk, your silent majority not so much.
Voluntary response surveys skew toward extreme opinions due to self-selection, whereas nonresponse bias stems from systematic differences between respondents and nonrespondents that affect representativeness, see comparison. (researchprospect.com)
Certainly! Here’s a section instructing readers—who may be new to HeySurvey—how to create a survey easily, in three steps, with bonus tips on branding and settings. This is suitable for including just above a “Use this template” button.
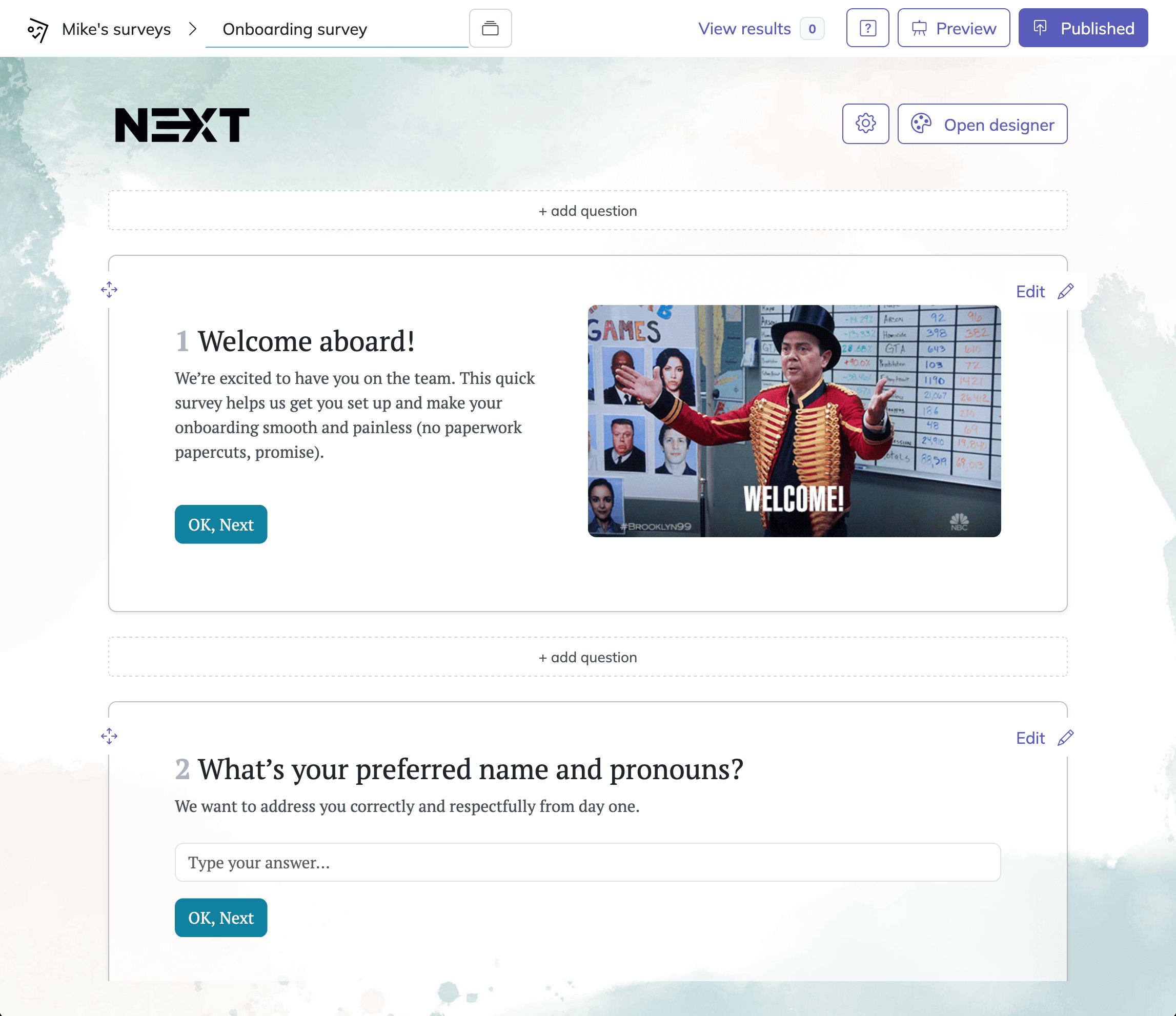
How to Create Your Survey with HeySurvey (In 3 Easy Steps)
Creating a survey on HeySurvey is quick and intuitive, even if it’s your very first time. Here’s how you can get started in just a few minutes with our online survey maker:
Step 1: Create a New Survey
Click the “Use this template” button below (or begin from the HeySurvey dashboard). You can either start with a ready-made template—which automatically loads relevant example questions—or choose to create a new survey from scratch. Next, you’ll see the Survey Editor, where you can name your survey for internal reference.
Step 2: Add Your Questions
Now, build your survey by adding questions. Click the Add Question button at the top or between any existing questions. HeySurvey lets you choose from a variety of question types, such as single or multiple choice, scales (e.g., 1–5), text answers, date pickers, or file uploads. For each question, simply enter the prompt, make it required or optional, and customize available answers. You can use images, markdown formatting, and even duplicate questions for quicker setup!
Step 3: Publish Your Survey
Once your questions are set, preview your survey to see how it will look. When you’re satisfied, click Publish. You'll be prompted to create (or sign in to) a free account to finalize this step. After publishing, you’ll get a shareable link for your audience—or you can embed the survey directly on your site.
Bonus Steps: Personalize and Configure
- Apply Your Branding: Open the Designer Sidebar to add your logo, change colors, adjust fonts, and set a background–ensuring your survey matches your organization’s style.
- Define Settings: Access the Settings Panel to set dates, limit responses, or add a custom “thank you” redirect URL.
- Add Branching Logic: For advanced flows, use branching so participants see only relevant questions based on their previous answers.
Now you’re ready—just click the button below to start your survey!
Incentivized Voluntary Response Surveys (Gift Cards, Loyalty Points)
Survey incentive wording can be your secret weapon, boosting replies and keeping data from drifting to lopsided extremes.
Why & When to Use
When you need answers but your crowd is not exactly chomping at the bit, you can sweeten the deal with an incentive.
Use this trick for post-event follow-ups, testing product samples, and longer surveys that need extra motivation, such as quality assurance survey questions.
It helps reduce nonresponse bias because more folks jump in, and everyone loves a freebie.
Incentives bring in the fence-sitters, not just the passionate ends of your audience.
On top of that, you just need to keep your offer clear and fair so you do not spark mistrust.
State the reward up front in plain English.
Keep the path to rewards simple, because if it feels like tax season, you will lose folks.
Ethical tip: Do not promise the moon and deliver a pebble.
5 Sample Questions
Please rate today’s webinar content quality.
How useful was the product sample you received last week?
Which reward level would most motivate you to complete future surveys?
What is the single biggest benefit you expect from our loyalty program?
If you could change one aspect of our checkout flow, what would it be?
Here is the thing, you still need to spot-check for voluntary response bias, because you might attract a certain “deal-seeker” personality, so call it out in your findings.
Small prepaid monetary incentives significantly boost voluntary survey response rates and can reduce nonresponse bias by encouraging participation from otherwise reluctant demographic groups (news.gallup.com).
Probability Sample Surveys With Potential Nonresponse Bias (Mail, Phone, Online Panels)
Non response bias vs voluntary response bias helps you separate good data from truly great data, especially when you care about serious research.
Why & When to Use
You use these when you want scientific-level accuracy for decisions that really matter.
You randomly select people, so every person in your target group has a genuine chance to answer.
Governments, academics, and political pollsters use these for accuracy, like census forms or election polling calls.
The problem shows up when some people simply do not respond, and that is where nonresponse bias sneaks in.
Here’s the thing: nonrespondents might quietly share a hidden trait that bends your results.
Maybe they do not trust surveys, maybe they work nights, or maybe they really hate phone calls.
If those missing voices would have changed the average, your results can take a serious nosedive.
Experts use statistical tricks like weighting and follow-up to fill in those gaps as much as possible.
Weighting means giving extra influence to answers from hard-to-reach groups so your sample better reflects reality.
On top of that, you should always report how many people skipped out and what you did to reach “the silent majority,” even if it felt like chasing ghosts.
5 Sample Questions
How many hours of paid work did you complete last week?
Which news source did you consult most yesterday?
What is your total household income before tax?
On a typical day, how many servings of fruit do you eat?
How satisfied are you with your current broadband speed?
Understanding the response vs nonresponse bias trade-off helps you choose the right survey method so you can trust your stats instead of just hoping they are right.
Follow-Up/Reminder Surveys for Nonrespondents
Nonresponse bias is a sneaky culprit, but targeted follow-ups help you catch quiet voices before they vanish.
Why & When to Use
When your initial invite flops or your favorite respondents ghost you, gentle reminders can still save your data day.
- Perfect for employee engagement checks, alumni fundraisers, and big customer campaigns.
- Focus on shrinking that nonresponse gap, because every “extra” reply helps balance the story.
- Mix your outreach: a text one week, a reminder email the next, and maybe even a cheerful phone call.
Just do not overdo it, because nobody likes a stalker, especially one with a survey link.
- Set a humane cadence with one nudge per week at most and rarely more than three tries.
- Keep it breezy and low-friction.
- Respect opt-outs religiously.
Here is the thing: You can ask nonresponders directly why they skipped the first round and learn a lot from their answers. For some inspiration, check out these quality assurance survey questions that are designed to be short and easy to answer, reducing friction for even the most hesitant respondents.
5 Sample Questions (shorter, friction-less)
In one word, how do you feel about our support team?
Did you find what you needed on our website today? Yes/No.
Select the statement that best describes your last delivery experience.
Would you like a callback to discuss your issue? Yes/No.
What kept you from responding to the first survey invitation?
Every rescued reply makes your survey story truer and your voluntary response bias vs nonresponse bias notes sharper, which is a pretty solid upgrade for a tiny reminder email.
Follow-up surveys using mode switching or shortened questionnaires can reduce nonresponse bias for some items, though paradoxically, they may increase total bias despite lowering both nonresponse and measurement error bias separately (academic.oup.com)
Mixed-Mode Surveys (Email + SMS + IVR + Web) to Reduce Nonresponse
Mixed-mode surveys help you tackle nonresponse bias with the same confidence you bring to fixing a wobbly chair with a full tool kit.
They are like a high-tech Swiss Army knife for your survey strategy.
Why & When to Use
Not everyone likes email, or phones, or apps, so you use every tool in your kit to reach a wide and wild audience.
You meet people where they already are, instead of begging them to come to you.
Use these when you’re surveying hard-to-reach folks, like busy patients, shift workers, or older adults.
They shine for big, ongoing efforts, such as municipal services, healthcare check-ins, and HR pulse checks.
The bonus is that you lower nonresponse bias by letting people pick their favorite reply method.
It’s like showing up to the party with chips, dip, and three different playlists, so no one can complain.
On top of that, you make it easy for every type of guest to feel included.
Here are perks:
Fewer coverage errors, so you avoid missing important demographic groups.
Letting each audience pick how they talk to you, which boosts comfort and honesty.
Here’s the thing: People sometimes answer differently by phone versus web, so “mode effects” are real.
Plus, the broader reach you gain can matter more than those small differences.
5 Sample Questions
Please confirm which contact channel you prefer for future surveys.
Rate your satisfaction with city recycling services.
Did you refill your prescription in the last 30 days? Yes/No.
How safe did you feel in the hospital during your stay?
Would you support an increase in local park funding? Yes/No/Unsure.
Non response bias vs voluntary response bias becomes a smaller headache when more people actually reply.
You get fewer crickets, more real voices, and a healthier mix of opinions.
Adaptive & Responsive-Design Surveys (Real-Time Bias Monitoring)
Response vs nonresponse bias dashboards are your behind-the-scenes secret for running modern, flexible surveys that practically tune themselves.
Why & When to Use
Imagine your survey platform watching replies in real time and nudging quotas so one group does not accidentally overpower the rest.
You use this for big, important projects like longitudinal studies, election exit polls, and brand trackers.
When you notice fewer teens replying, the system can re-balance by pinging more of them until samples match your target.
Plus, you get paradata insights that act like secret stats, showing who answers, when they answer, and on what device.
You are not just collecting data; you are steering it with a pretty steady hand.
Every new answer tweaks your targets for accuracy on the fly.
This method automates what humans used to check manually, which makes it faster and less error-prone.
On top of that, when you see stubborn gaps, you can dig deeper and craft new invites aimed exactly where they are needed.
5 Sample Questions
Since our last interview, have you changed jobs? Yes/No.
Which candidate do you lean toward today?
Compared with last month, is your household’s financial situation better, worse, or the same?
How often did you stream video content yesterday?
What device are you using right now to complete this survey?
Here is the thing: you always know how much voluntary response bias vs nonresponse bias you are facing, almost minute by minute.
Dos and Don’ts: Best Practices for Minimizing Voluntary Response & Nonresponse Bias
You can treat voluntary response bias vs nonresponse bias as your cue to survey smarter, not as a showdown.
Do
Pretest your opt-in and invitation wording with real users before launch so you can catch confusion early.
Randomize answer order so no choice gets the easy “first spot” advantage and quietly wins.
Offer incentives that are equitable and clearly explained, like “$10 for 5 minutes,” not “maybe you’ll win one day!”
Mix up your modes: web, phone, apps, and mail all have fans, and you want as many of them as possible.
Always disclose risks of bias and survey limitations in your report so your readers never get surprised later.
Don’t
Over-survey the same group, because burnout leads to both nonresponse bias and cranky replies you do not want in your dataset.
Hide the details or small print about incentives, since surprises feel fun in games but not in research.
Ignore paradata, because “how” and “who” replied can outshine the “what” when you interpret results.
Assume no reply means “they’re happy” or neutral; silence is ambiguous and often misleading.
Use only open “call-in” surveys if you want true population insight, unless you enjoy hearing only from the loudest voices.
Here’s your rapid-fire checklist:
Flag opt-in surveys as at risk for voluntary response bias so you can plan controls in advance.
Use reminders and incentives to shrink nonresponse bias and pull in quieter participants.
Mix up your survey modes to cut coverage errors and reach people where they actually are.
Monitor replies live, then adjust quotas fast when certain groups lag behind.
Report all bias risks and correction methods so others can judge how solid your findings really are.
You deal with voluntary response bias whenever you mainly hear from people who eagerly raise their hands, and you face nonresponse bias when whole groups stay silent.
Both can twist your results for different reasons, with one driven by loud opinions and the other by missing data that quietly distorts the picture.
Plus, your research needs come first, so you pick your audience, weigh your risks, then choose your technique accordingly.
Want better accuracy that people trust?
On top of that, you test your invites, fine-tune your incentives, and always show how you handled the bias so your research and decisions can stand up to tough questions.
Best Practices: Dos & Don’ts for Minimizing Nonresponse and Voluntary Response Bias
If you want your surveys bias-resistant and your data deliciously accurate, you need to lock in a few simple habits.
Top Dos
Use clear, jargon-free language.
Personalize your invitations.
Offer multi-language options.
Keep it short and sweet.
Ask for feedback at multiple touchpoints.
Follow up with nonresponders, and keep it gentle.
Pre-test your survey on a small group.
Use mixed modes when possible.
Offer relevant, not excessive, incentives.
Emphasize why their voice matters.
Make opt-out simple and obvious.
Update contact lists regularly.
Typical Don’ts
Don’t over-incentivize, because cheaters really do show up for free stuff.
Don’t force participation; invite, do not insist.
Don’t bury the opt-out or privacy info.
Don’t use loaded or leading questions.
Don’t make the survey too long.
Don’t assume one email reaches all.
Don’t neglect mobile compatibility.
Don’t ignore follow-up opportunities.
Don’t target only your “ideal” respondents.
Don’t complicate incentives.
Don’t forget to thank participants.
Don’t just look at response rate; check balance across groups.
Here’s the thing: choosing the right survey style means you understand nonresponse vs voluntary response bias inside and out.
On top of that, you can always circle back to the survey types above if you want a quick bias-busting blueprint.
FAQ time! If you are wondering “what is voluntary response bias definition,” it is the tilt in your results when only self-motivated folks answer your survey.
Plus, if you ask “what are nonresponse bias examples,” think customer email surveys where about 90% ignore you, or census updates where entire neighborhoods quietly bow out.
If you have the itch to know “how to avoid voluntary response bias,” you should pick fair samples and skip all-comers polls whenever the data really matters.
On top of that, you can mix your modes and always chase the voices you might be missing so your numbers stay honest.
Choosing the Right Survey Strategy for Your Research Goals
When you pick a survey method, you are basically choosing the right tool for your job as a researcher. Your survey strategy should match your research goal.
Nonresponse Follow-Up Survey: You use this when you want to boost response rates in mandatory studies and gently nudge people who did not respond the first time.
Voluntary Response Survey: This works well when you want to capture spontaneous feedback from people who are already motivated to share their opinions.
Mixed-Mode Survey: You choose this when you need to reach a broad, diverse audience by combining methods like online, phone, or mail.
Incentivized Survey: This shines when you need detailed insights and can offer rewards, since people usually give better answers when there is something in it for them.
Panel Retention Survey: You rely on this for ongoing studies with the same group, so you can keep participants engaged and coming back.
Randomized Response Survey: You turn to this for sensitive topics that require honest answers, since it helps people feel safer telling the truth.
Best Practices: Dos and Don’ts to Minimize Nonresponse & Voluntary Response Bias
Smart survey habits make your data way more trustworthy.
Do:
Keep Surveys Concise: You respect your respondents' time when you keep your questions focused and necessary.
Personalize Invites: You make participants feel valued when you use their name and speak directly to their interests.
Test Incentives: You can experiment with rewards to see what actually motivates your specific audience.
Diversify Channels: You reach people where they already are when you use email, social media, SMS, and other platforms.
Monitor Drop-Off Points: You quickly spot where participants lose interest when you track where they stop answering.
Don’t:
Ignore Reminder Timing: You avoid annoying or losing your audience when you time reminders thoughtfully instead of bombarding or neglecting them.
Overload with Open-Ended Questions: You keep people from burning out when you balance open-ended items with easier, quicker questions.
Rely on a Single Mode: You connect with more types of respondents when you mix survey modes instead of using only one.
Forget Mobile Optimization: You make your survey accessible for busy people on the go when you ensure it works well on all devices.
Skip Bias Analysis: You protect your results from sneaky distortions when you always check for potential biases.
On top of that, when you understand and address nonresponse bias and voluntary response bias, you can design surveys that deliver accurate, actionable insights. Remember, the quality of your data shapes the quality of your decisions, so treat each survey like it matters, because it does.
Related Business Survey Surveys
29 Essential SWOT Survey Questions for Strategic Insights
Discover 25+ expert SWOT survey questions designed to capture strengths, weaknesses, opportunitie...

29 Quality Assurance Survey Questions for Effective Feedback
Discover 25 quality assurance survey questions to boost your QA process. Explore expert sample qu...
33 Sustainability Survey Questions: Types, Use Cases & Samples
Explore 8 types of sustainability survey questions with 25+ sample questions to uncover insights ...